| 1. What is Hylaluronic Acid? |
Hyaluronic Acid occurs in living tissue and is an important component of connective tissue. Its main function is to aid in the body’s water maintenance by binding water molecules to our tissues. As we age, the amounts of Hyaluronic Acid in our tissues deteriorate and contribute to joint ailments and other physical ailments such as wrinkles. By drawing in and holding onto water in the outer cell layers of the skin, hyaluronic acid allows for a vital process that enables effective skin hydration, delivery of nutrients, and removal of contaminants and other toxins. It’s functional properties and its consistency allows Hyaluronic Acid to be used as a moisturizing agent in skin care products.Hyaluronic Acid is one of nature’s most hydrophilic molecules and is often described as nature’s natural moisturizers. |
| 2. What is its Chemical Structure? |
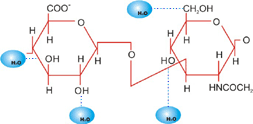
- Hyaluronic Acid is classified as carbohydrate, more specifically it is known as a mucopolysaccharide, which is a chain of thousands of sugars long. The unique thing about Hyaluronic Acid is that when it is not bound to sugar molecules, it binds to water. This creates a viscous jelly like fluid that can function in many areas. Its main functions are to bind water and lubricate movable parts of the body. The molecule is made of repetitive sequences of 2 sugars: one strand is called gluconic acid and the other called N-acetyl glucosamine. These compounds are both negatively charged and repel each other to produce a long, stretched out molecule. This results in a molecule that is long and large in size with high viscosity. These properties allow it to become highly compressible and be able to withstand the tension of everyday activity that can jolt the joints. This is why it can be used to protect our joints and skin tissue. |
| 3. Where is it located in the body? |
-Hyaluronic Acid is naturally found in almost every cell of the body, but is found in high concentrations in certain parts of the body. Hyaluronic Acid is found in bones and cartilage, tendons and ligaments, and in lips and eyes. Hyaluronic Acid is also a major component of skin tissue and is found in greatest concentration in the skin. It is found in the deeper dermal layers of skin as well as the visible layer of the epidermis. Hyaluronic Acid is able to continually moisturize the skin by binding up to 1000 times its weight in water. The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a gelatinous fluid that surrounds the cell and aids in everyday cellular function. Hyaluronic Acid’s role is to support the stretchy fibers and prevent the overstretching of fibers as well as continuously providing moisture so the skin would not dry out. It serves different functions in different part of the body. Unfortunately, Hyaluronic Acid has a short half life of 3 days in the body and approximately 1 day in the skin. This is why the body needs to continually replenish their supply of Hyaluronic Acid. |
| 4. How does Hyaluronic Acid Help the skin? |
-The skin is known as the largest organ in the body and comprises 15% of the body’s weight. Roughly 50% of the Hyaluronic Acid in the body is found in the skin. Hyaluronic Acid is found in both the skin’s dermis and epidermis. Elastin and Collagen and Hyaluronic Acid are components that are essential to the health of our skin. Although collagen provides the support for the skin, it is hyaluronic acid that nourishes and hydrates it. If Elastin (which keeps skin elastic) is not hydrated it would eventually be overstretched and dried out and will not support the skin as well. Collagen is constantly submerged by Hyaluronic Acid’s gelatinous substance and keeps collagen moist and elastic. Young skin is smooth and elastic due to high concentrations of hyaluronic acid. With age, hyaluronic acid deteriorates and loses its ability to restore itself and can leave the skin looking unhealthy and wrinkled. Thus with external products, we can constantly replenish the skin’s supply of Hyaluronic Acid and keep our skin looking smooth and young. |

